
- #Git add remote origin master how to#
- #Git add remote origin master software#
- #Git add remote origin master code#
- #Git add remote origin master mac#
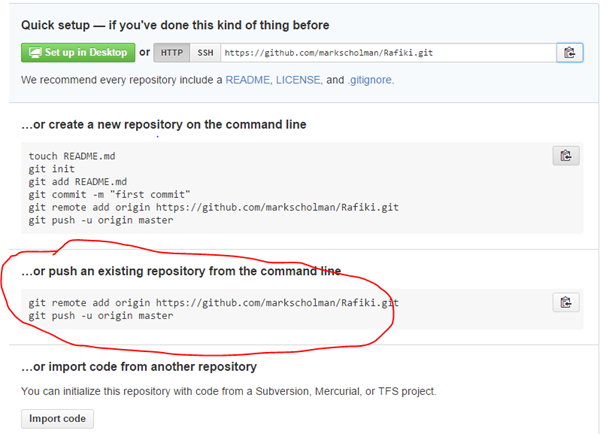
This time, replace your-remote-url with the Bitbucket remote URL. For example, to add a remote from Bitbucket to your repo, run the following command: You can add more remotes to the same Git repo by specifying a different shortname for the new remote. You should get an output that looks like this: To verify that everything ran successfully, run this command: The word "origin" in the command above serves as a shortname for the new remote. The command above should add a new remote to your local repo. Go to the command prompt or terminal, and from the root directory of your project, run the following command (replace your-remote-url with the valid URL for your repo): Now let's add the remote URL to our local repo. Step 3: Adding Remote URL To a Local RepoĪt this point, we have a local Git repo, a remote Git repo, and the URL for our remote. You will be required to enter the remote URL in the next step. Please make sure to note the remote URL (GitHub and Bitbucket) for your repo. The remote URL for a GitHub repo looks like this. Just like Bitbucket, you should also be greeted with a page that shows a remote URL for the new repo. Leave all other options unchanged and click on the green Create repository button at the bottom of the page.Īn empty GitHub repo will be set up. On the Create new repository page, enter a repository name of your choice. Log in to GitHub and click on the + icon in the top navigation bar, then click on New repository. Once your empty remote repo is created, Bitbucket should greet you with a page that shows the remote URL for the new repo.īitbucket provides a remote URL that looks like the following link: 2.2: Creating a New Repo on GitHub When you are done, click the Create repository button to finish the process. Doing so will set up an empty remote repo that is ready to be connected to your local repo. After that, set the options for both Include a README and Include. In the Create new repository page, specify your project name and repository name. Log in to Bitbucket, go to the repository section in the user dashboard, and click on the Create repository link. The process for setting up a new repo in Bitbucket and GitHub is described below. This step is important if you do not already have a remote that you wish to add to your repo. Now let's create a remote repo and retrieve the Git URL for the remote repo. In the previous step, we created a new local Git repo. Git does not auto-save changes to your project. Commits are like save points in a video game. The first command adds all your project files to Git, while the second command creates a commit.Īt this point, you have initialized Git in your project and made your first commit. Run the following commands to add your project files to the Git repo and make your first commit: The above command should create a local Git repo for your project if executed successfully.Ī few further actions. Next, run the following command to initialize Git: For example, if your project is stored in "/Users/you/document/hello-world," you will run the following command to change the working directory:Ĭhange "/Users/you/document/hello-world" to the current directory for your project. Open a new command prompt or terminal window and change the working directory to the root directory of your project. Otherwise, follow the instructions below to get started.
#Git add remote origin master how to#
If you already have a local Git repo and just want to learn how to add a new remote to it, you can skip this step and jump to step 2. We will need a local Git repo to which we will be adding the new remote. This post assumes that you already have Git installed on your local machine. The first requirement is the local Git repo that we'll be adding a new remote to. In the first two steps in this post, we will set up some of the basic things necessary before we can add a new remote to a Git repo. We will start by adding Git to a new or existing project and conclude by sharing the project to a Git hosting service like Bitbucket and GitHub. In this post, you will learn how to set up remotes for your local Git repo in three steps. Git remote makes it easy for developers to collaborate. The repository could be private, public, or on some server you control.
#Git add remote origin master code#
With Git remote, you can share your code to a remote repository.
#Git add remote origin master mac#
Git is available for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. With Git, you can save the state of your code at regular intervals (determined by you).
#Git add remote origin master software#
Git remote is an important part of Git, a tool that provides an easy-to-use system for tracking changes in source code during software development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
